

Fate has not been kind to the San Joaquin kit fox (Vulpes macrotis mutica).
Shrinking habitat caused by urbanization and agricultural expansion landed this Central Valley native on the federal Endangered Species List decades ago. California’s total population of San Joaquin kit foxes may now be down to a few thousand animals. To make matters worse, its favorite food, the kangaroo rat, is likewise endangered as the desert habitat it prefers continues to disappear.
Wildlife biologists took heart, however, in a population that seemed to be thriving within the city limits of Bakersfield. Unlike San Joaquin kit fox populations in other parts of the Central Valley range, the Bakersfield foxes adapted quite nicely to urban life. Their number – estimated between 200 and 400 animals – has evidently seemed to be holding steady and possibly increasing.
Their cute and cuddly appearance make them popular with city residents. Earlier research showed the population was healthy and genetically robust. Wildlife biologists were counting on those urban foxes to ensure the species’ survival should kit fox populations completely collapse elsewhere.
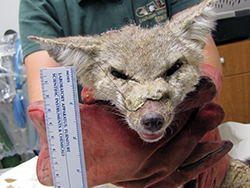
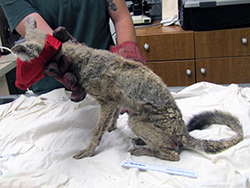
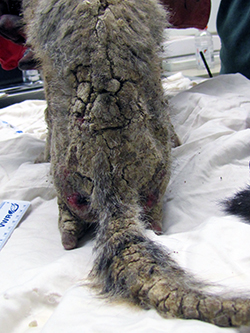
Today, those Bakersfield kit foxes are under siege, suffering from an outbreak of highly infectious sarcoptic mange. Mange – a skin condition caused by parasitic mites -- leads to hair loss, open wounds from scratching and, ultimately, death. The first case was detected among the kit fox population in March 2013, and since then, more than 200 cases have been documented. The epidemic has grown worse every year.
Given the importance of the Bakersfield population, CDFW, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, the California State University, Stanislaus, the University of California, Davis (UCD), and various nonprofit wildlife groups have all joined forces to combat the mange.
Jaime Rudd, an environmental scientist in CDFW’s Wildlife Investigations Lab in Sacramento, is leading CDFW’s efforts while simultaneously writing her UCD Ph.D. dissertation on the outbreak. Rudd is researching ways to prevent mange from spreading to healthy animals, and assisting Stanislaus State’s Endangered Species Recovery Program with trapping and treating diseased foxes.
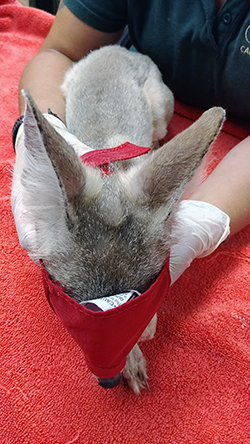
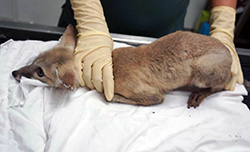
Severely diseased kit foxes are trapped and transported to the California Living Museum, a Bakersfield wildlife rehabilitation facility and zoo. There, the kit foxes are hospitalized, given life-saving antibiotics and fluids and treated with a topical pet product that kills the mites. The foxes often need months of treatment before they are healthy enough to release. And although the intervention saves individual lives, the process is costly and time-consuming – and doesn’t prevent the treated fox from getting mange a second or third time.
Rudd is making good use of her undergraduate degree in molecular biology, analyzing the DNA of the mites to see if they might be related to those in dogs and coyotes, which could be spreading the mange to the foxes.
“Essentially, we want to look at their molecular signature to see if these mites are related,” Rudd said.
Rudd is studying a group of wild kit foxes living on the CSU Bakersfield campus, which no doubt are supplementing their diet with burger bits and pizza crusts discarded by college students. Rudd is monitoring the group with trail cameras, outfitting some foxes with radio tracking collars and others with the type of preventative flea and tick collar you might use on a pet dog or cat.
“We want to evaluate the efficacy of these collars,” she said. “If they’re only going to work for two months, the collars won’t help us slow down the spread of mange, so is it really worth the effort of putting them on? But if they’re going to work for five months or more, then it might be worth the effort.”
If there is any hope sustaining Rudd and her colleagues in this important, though often disheartening, work, it’s this: “The fact we are not seeing mange in the outlying populations is cause for optimism,” she said. “If nothing else, we can at least try to keep it from leaving the city.”
The top photo is a female San Joaquin kit fox with sarcoptic mange. The next six photos show a progression of mange in one of Jaime Rudd’s Bakersfield study animals, a male kit fox. The photos show a healthy animal in January 2017 before getting mange. The next three shots show him infected with mange in July 2017. The next two are four weeks after treatment for mange in August 2017. CDFW photos by Jaime Rudd.
The last photo is another kit fox, six weeks after treatment. Photo by Erica Kelly, Endangered Species Recovery Program (ESRP), a multi-agency/university program at CSU Stanislaus.
To see CDFW Scientific Aide Megan O’Connor release a treated San Joaquin kit fox back to the CSU Bakersfield campus, click here.