
CDFW manages about 940,000 acres in over 200 properties statewide that are designated as wildlife areas or ecological reserves. Pictured is Elkhorn Slough Ecological Reserve in Monterey County.
Properties like the Carlsbad Highlands Ecological Reserve are acquired and managed to protect sensitive plant and wildlife species.

At the nearly 17,000-acre Yolo Bypass Wildlife Area near Davis, staff close off some areas to the public during certain times of year. The closed zones offer resident wildlife a reprieve from the many activities offered at the site such as hunting, wildlife viewing, and student education field trips.
CDFW working to improve negative effects of non-consumptive recreation on conservation
Editor’s Note: As we publish this article, California, the nation, and the whole world are gripped by the COVID-19 pandemic. To slow its spread and not overwhelm healthcare resources, distancing and stay-at-home orders have led to the delay of trout openers and other fishing events, and closure of parks, reserves and many other publicly accessible facilities. Stories are beginning to emerge of increased wildlife presence in park and reserve areas that are normally filled with people. We look forward to the end of the pandemic and its horrible devastation will be over very soon but we know it will be some time before we realize a return to “normal.” We hope to gain from this emergency more information on wildlife’s response to fewer visitors – data that may be able to help us improve our management of parks and reserves in a way that protects wildlife and their habitat while also providing reasonable recreation experiences. In the meantime, stay well, and stay home to save lives.
Do Not Feed Wildlife. Do Not Cut Switchbacks. Stay On Trail.
If you’ve spent time in recreational areas, you’ve seen the signs. You’ve most likely complied with them. But you may not have a full understanding of why the rules are important.
A growing body of research is showing that non-consumptive recreation – i.e., activities like hiking, biking and bird watching, that don’t involve harvesting of resources – can have harmful effects on species, their habitat and efforts to protect them.
For example,  one study showed that mule deer may experience increased predation risk when they shifted toward nocturnal activity in response to human recreation. Another study showed that human activity resulted in elk foraging less and showing increased signs of stress.
one study showed that mule deer may experience increased predation risk when they shifted toward nocturnal activity in response to human recreation. Another study showed that human activity resulted in elk foraging less and showing increased signs of stress.  Research has shown (PDF) that higher levels of human activity reduced habitat suitability for bobcats, gray fox, mule deer and raccoons. Human activity has also been linked to declines in reptile species.
Research has shown (PDF) that higher levels of human activity reduced habitat suitability for bobcats, gray fox, mule deer and raccoons. Human activity has also been linked to declines in reptile species.
Recreation  has been cited as a factor in endangerment of plant and animal species on federal lands, and of all U.S. states, California has the
has been cited as a factor in endangerment of plant and animal species on federal lands, and of all U.S. states, California has the greatest number of listed species that are threatened by recreation. In a
greatest number of listed species that are threatened by recreation. In a  literature review led by Courtney Larson, a scientist for The Nature Conservancy, 93 percent of included articles found significant effects of recreation on wildlife.
literature review led by Courtney Larson, a scientist for The Nature Conservancy, 93 percent of included articles found significant effects of recreation on wildlife.
“CDFW is tasked with managing the state’s diverse plant and wildlife species and the public’s use and enjoyment of them – so how do we also manage the effects of recreation? We have to bring environmental stewardship into the fold and find ways for recreation and conservation groups to work together,” said Ron Unger, a program manager in CDFW’s Habitat Conservation Planning Branch. “It’s important to set aside lands for both needs. Lands set aside for conserving declining and vulnerable species generally need to be restricted in terms of public access. Other, less sensitive sites need to be set aside so people can have a positive place to enjoy and appreciate nature and the outdoors.”
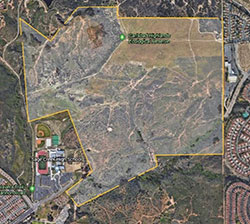
At the Carlsbad Highlands Ecological Reserve – a CDFW-owned reserve in San Diego County – land managers have had a tough time with mountain bikers and others building illegal trails. Over the past half-dozen years, bikers have illegally carved out about 17 miles of trails (the property has 2.1 miles of legal trails) and removed nearly 500 trail signs. CDFW had to  step up enforcement to stop the illegal trail use.
step up enforcement to stop the illegal trail use.
“We don’t enjoy telling people they can’t ride here, but at the same time we have to make sure we don’t love these spaces to death – especially when the main reason the lands are acquired and set aside is to protect wildlife,” said CDFW Regional Manager Ed Pert.
At the nearly 17,000-acre Yolo Bypass Wildlife Area near Davis, staff close off some areas to the public during certain times of year. The closed zones offer resident wildlife a reprieve from human activity.
“It’s definitely a balance. We want the public to enjoy wildlife, but we also want to give wildlife a place to rest,” said Joe Hobbs, who manages the wildlife area.
CDFW Senior Environmental Scientist Shannon Lucas helps coordinate the department’s Natural Community Conservation Planning (NCCP) program, which issues regional permits that allow for development while ensuring habitat protection. She also oversaw grant funding for research on the effects of recreation on NCCP lands.
“These are areas that are intended to be preserved for their ecological value. We have a responsibility to analyze the effects of recreation on the species and habitats that contribute to conservation under an NCCP,” said Lucas.
CDFW is involved with research efforts aimed at gaining insight into how to best balance recreation with conservation. The department’s Human Dimensions of Wildlife Unit is currently researching the views of stakeholders, and future research will assess how to best communicate with stakeholders on the issue.
“We want to serve our constituents as well as manage the state’s natural resources for their ecological value. Once we understand how our stakeholders feel about the issue, we can communicate in a way that connects with their concerns,” said lead researcher Alex Heeren.
CDFW just released a special edition scientific journal featuring literature reviews and original research on the effects of non-consumptive recreation on wildlife. Ange Baker, editor-in-chief of California Fish and Wildlife Journal, chose the topic after soliciting ideas from CDFW employees.
“Research has shown that even mild recreation like hiking can have pretty significant impacts on some species. This is an especially important issue in California where CDFW manages about 940,000 acres of property designated as wildlife areas or ecological reserves. We decided to do a special edition to bring light to the issue,” said Baker.
 Read the special edition journal (PDF).
Read the special edition journal (PDF).
CDFW Photo. Top Photo: Signage at Carlsbad Highlands Ecological Reserve in San Diego County is intended to help protect threatened and endangered plant and wildlife species by prohibiting incompatible recreation activities such as motorized vehicle, biking, and drones.
Media Contact:
Ken Paglia, CDFW Communications, (916) 322-8958