(Acanthomintha ilicifolia)
 Acanthomintha ilicifolia. Photo by Jeb Bjerke (cc).
Acanthomintha ilicifolia. Photo by Jeb Bjerke (cc).
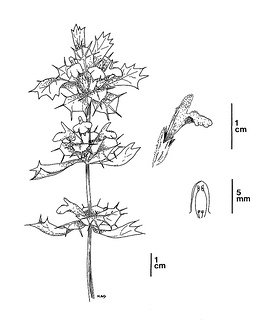 Acanthomintha ilicifolia. CDFW illustration by Mary Ann Showers. (Click to enlarge)
Acanthomintha ilicifolia. CDFW illustration by Mary Ann Showers. (Click to enlarge)
San Diego thornmint is a California endangered plant species, which means that killing or possessing this plant is prohibited by the California Endangered Species Act (CESA). San Diego thornmint is an annual species that only occurs naturally in southwestern San Diego County and northern Baja California in openings within coastal sage scrub, chaparral, and native grassland. The species is also restricted to certain gabbro and calcareous clay soils on gentle southeast to west facing slopes and blooms April through June. San Diego thornmint is also listed as a threatened species under the federal Endangered Species Act, and at the time of this page’s posting, the California Natura Diversity Database reports 59 occurrences of this species that are presumed to still exist.
Urbanization is the factor responsible for most of the populations of San Diego thornmint that have already been destroyed. Although urbanization was the greatest threat to San Diego thornmint in the past, this threat has been somewhat reduced now that approximately 70 percent of remaining populations have been protected from development. Despite these protections, however, San Diego thornmint continues to be in danger of extinction. Invasive species present a pervasive threat to San Diego thornmint, and over 60 percent of extant populations are in close proximity to development, agricultural fields, fuel modification zones, or other regular disturbance. The species continues to be threatened with the direct and indirect effects from urbanization, off-road vehicle use, invasive species, fire, and climate change, and also because of the vulnerability of small plant populations.
Several actions should be accomplished to conserve San Diego thornmint. These include conserving and managing unprotected populations in cooperation with landowners; restoring populations impacted by off road vehicle use and other impacts; coordinating San Diego thornmint monitoring efforts; and studying San Diego thornmint pollination, seed set, and threats to the species such as climate change.
CDFW has participated in the following San Diego thornmint studies and papers through participation in the Cooperative Endangered Species Conservation Fund or other mechanisms:
CDFW may issue permits for San Diego thornmint pursuant to CESA, and you can learn more about the California laws protecting San Diego thornmint and other California native plants. Populations of San Diego thornmint occur in CDFW’s South Coast Region. More information is also available from the United States Fish and Wildlife Service Species Profile for San Diego thornmint.
Updated 1/17/2013