The California Department of Fish and Wildlife is dedicated to excellent stewardship of the data it collects. The Department's approach to governance of scientific data is designed to:
- Increase the internal sharing and public dissemination of scientific data
- Limit and document the withholding of scientific data
- Ensure the proper documentation, storage, and security of scientific data
- Ensure that scientific data are treated as a mission-critical asset
- Align our data management practices with Open Data Objectives, which include; increasing transparency and accountability, increasing efficiencies through greater exchange of scientific data, engaging citizens to help improve public services, and promoting economic growth and innovation
The Department contributes to these goals by:
- Centralizing the documentation of scientific data in the Department with simple Data Management Plans (DMPs) for all scientific data projects
- Promoting data entry into the California Natural Diversity Database (CNDDB), which is the state's repository for information on rare plants and animals
- Requiring that scientific data are made public unless withholding the data is in the best interest of the resource, withholding data is required by law or regulation, or there are other compelling reasons to withhold it
- Ensuring that standardized metadata is developed for all scientific data
- Ensuring that all contracts with a scientific data component include any data as a contract deliverable
The Data Management Plan or DMP is a metadata framework through which CDFW manages scientific data internally. DMPs are developed for all scientific data and allow tracking of key attributes, such as species, methods, timeframes and contact person. DMPs and associated data are then centralized and, when appropriate, published to the Natural Resources Agency Open Data Portal and the California Open Data Portal
The CNDDB Program mission is to advance conservation of California's at-risk ecological resources through collecting, synthesizing, and sharing biological information. The CNDDB program is subscription-based and distributes textual data via the online application RareFind and distributes spatial data via Geographic Information Systems (GIS) products. In addition, users without GIS software can view CNDDB spatial data through the Department's online map viewer, BIOS.
The diagram below outlines the workflow that CDFW Data Management staff follow once staff provide their data paired with a DMP.
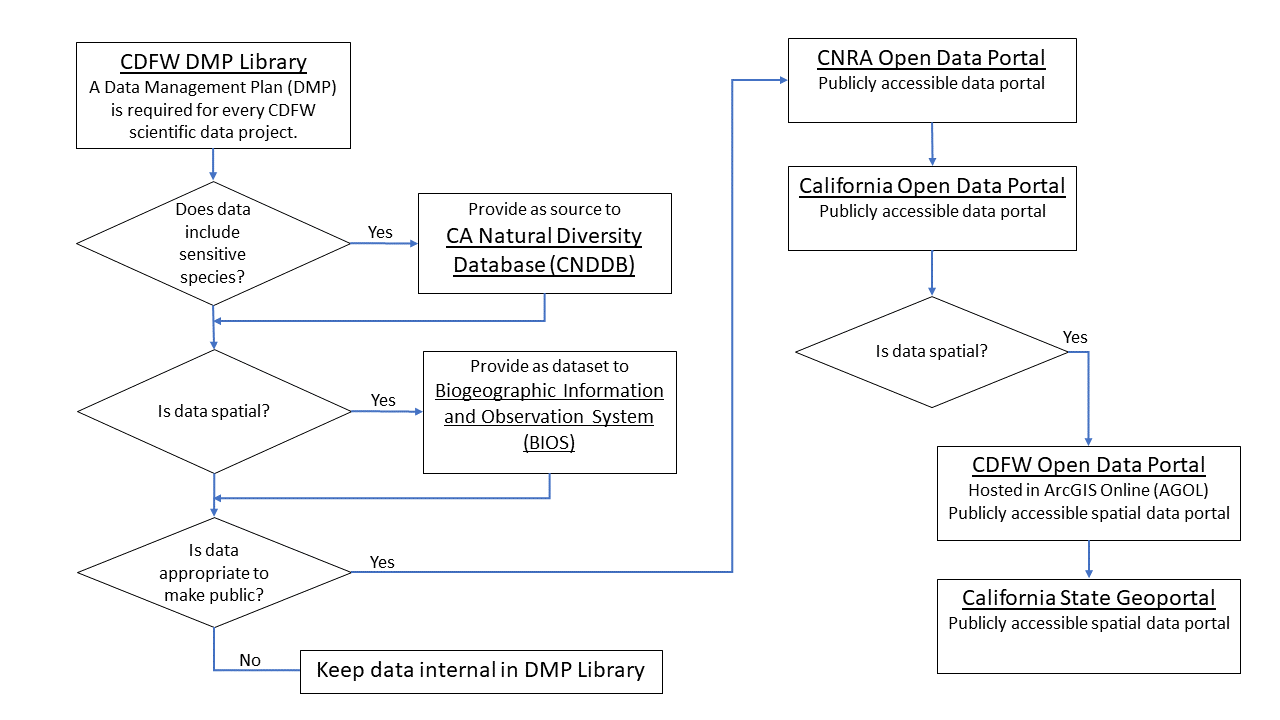
The diagram above shows how CDFW manages scientific data. Initially, a CDFW employee creates and submits a DMP describing the data into the internal CDFW DMP Library. The data are then processed as follows:
- If the data are related to sensitive species, they are submitted to the California Natural Diversity Database, a CDFW repository for such information.
- If the data are both spatial and biogeographic, the data are submitted to BIOS, a CDFW Geographic Information System which allows either public or internal CDFW access to data, depending on its sensitivity.
- If the data are not appropriate for the public (i.e., contain sensitive data that could harm species or violate people’s privacy), then they are stored internally.
- If the data are deemed suitable for public release, they are submitted to the California Natural Resources Agency Open Data Portal, then automatically submitted to the California Open Data Portal.
- Finally, if the data are geospatial and appropriate for public release, they are also submitted to the CDFW Open Data Portal (a public ArcGIS Online data portal) and then to the California State Geoportal.
Data Sources