Oncorhynchus mykiss irideus
 © Mark Jessop, all rights reserved.
© Mark Jessop, all rights reserved.
Distribution and Habitat
In North America, coastal rainbow trout are native to Pacific coast streams, from the Kuskokwim River in Alaska south to Baja California. In California, coastal rainbow trout are the most widely-distributed native trout form and are found on the western slopes of the Sierra Nevada in waters draining to the Pacific Ocean. Widespread glaciation that occurred over 10,000 years ago likely limited coastal rainbow trout distribution to elevations less than 8,000 feet on the west slope of the Sierra Nevada (probably lower elevations in the northern part of the range).
However, upstream distribution within this portion of their historic range is largely unknown and probably varied from stream to stream. Whether a given population was able to ascend these streams likely depended on the location of impassable barriers, rather than a specific elevation.
 © Mark Jessop, all rights reserved.
© Mark Jessop, all rights reserved.
Threats
Wild, naturally-spawning resident coastal rainbow trout are likely much more abundant now than historically because of their wide-spread introduction into most suitable waters in the state, including reservoirs. Tailwater fisheries below large dams often provide excellent habitat conditions with stable flow and water temperatures. While local populations in urban and agricultural areas may be diminished or even eliminated, total abundance statewide is high.
However, the anadromous life history form (steelhead) is severely impacted by dams, development, urbanization, water diversions, timber harvest, agriculture, and other land use practices across the state.
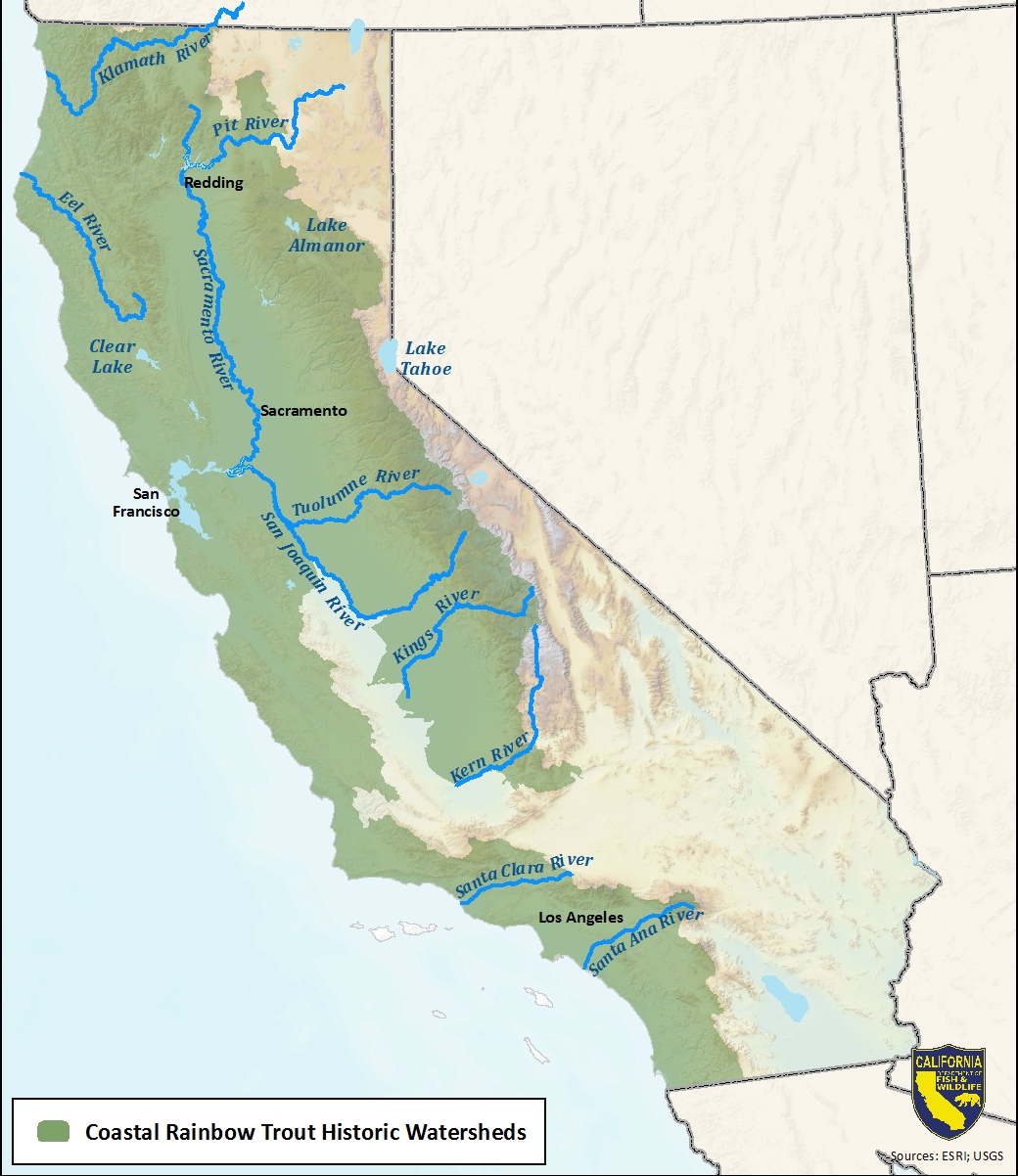 Map of coastal rainbow trout historic watersheds.
Map of coastal rainbow trout historic watersheds.
Conservation and Management
Most conservation actions are focused on bolstering anadromous populations via hatchery propagation, release of juvenile steelhead, and habitat restoration. However, large dams in most rivers and streams within the historic range of steelhead prevent access to a majority of the historic spawning grounds. This impedes restoration, particularly given that dams provide stable downstream tailwater habitats that generally favor the stream-resident, rather than anadromous, life history pattern.
Species Status
Most steelhead populations in California are endangered or threatened under the Federal Endangered Species Act.